One of the goals of Movable Party is to provide an interactive experience for audiences/participants. Since power will be generated from a hub motor attached to the rear wheel of each bike (see this post), the speed of the rear wheel directly translates to the amount of power generated. Detecting how fast the rear wheel is moving thus seems like the most obvious/important piece of data to capture from these stationary, power-generating bikes.
Tachometer
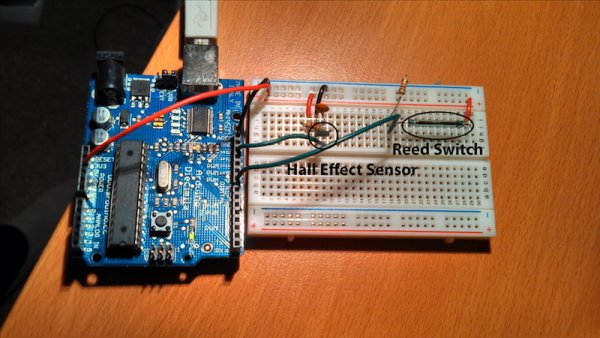
The easiest way to detect the speed of the rear wheel (the way most bike computers work), is to make a tachometer–simply put, a revolution counter. By counting the number of revolutions over a certain period of time, we can determine how fast the wheel is turning. Basically, you want to count the number of times a specific spot on the wheel crosses a point of measurement, and divide by some time constant (e.g. Revolutions per Minute, RPMs). Electronically, you are triggering a switch every time this point on the wheel passes a fixed sensor.
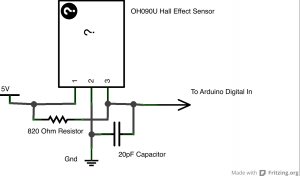
Because the wheel is turning and the sensor is fixed, using a mechanical switch where there is contact every rotation will not work very well. For example, the mechanical switch will cause friction every rotation. Also, maintaining perfect distance between the wheel and the switch will be difficult. Instead, there are two common ways of detecting rotation that do not require contact between the sensor and the wheel–optically and magnetically. Due to my own personal familiarity with magnetic circuits, as well as the expense of using an optical system and concerns about the functionality of that system in ambient light, I have decided to pursue magnetic sensing.
Read more: Rear Wheel Tachometer
